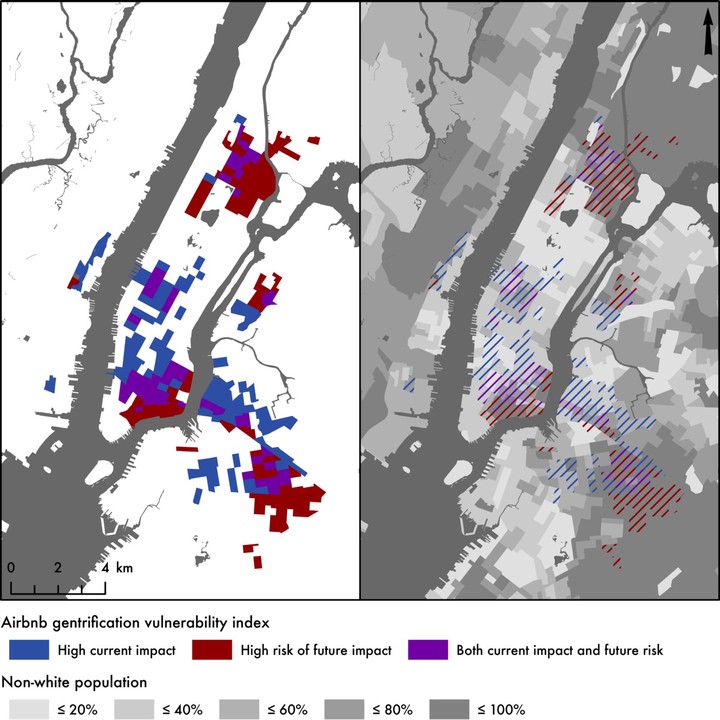
Abstract
Airbnb and other short-term rental services are a topic of increasing concern for urban researchers, policymakers, and activists, because of the fear that short-term rentals are facilitating gentrification. This article presents a framework for analyzing the relationship between short-term rentals and gentrification, an exploratory case study of New York City, and an agenda for future research. We argue that Airbnb has introduced a new potential revenue flow into housing markets which is systematic but geographically uneven, creating a new form of rent gap in culturally desirable and internationally recognizable neighborhoods. This rent gap can emerge quickly—in advance of any declining property income—and requires minimal new capital to be exploited by a range of different housing actors, from developers to landlords, tenants, and homeowners. Performing spatial analysis on three years of Airbnb activity in New York City, we measure new capital flows into the short-term rental market, identify neighborhoods whose housing markets have already been significantly impacted by short term rentals, identify neighborhoods which are increasingly under threat of Airbnb-induced gentrification, and estimate the amount of rental housing lost to Airbnb. Finally, we conclude by offering a research agenda on gentrification and the sharing economy.